Solution Details
Current Transformer (Sensor) Detection Solution
1. Introduction
Current transformers (sensors), as crucial equipment in power systems, have performance reliability and accuracy that play a decisive role in the safe and stable operation of power systems and the precise measurement of electric energy. With continuous innovations in power technology, various new types of current transformers have emerged, and corresponding testing technologies and equipment are also continuously developing.
2. Relevant Regulations and Standards
(1) National Metrology Verification Regulations
1. JJG 1189.3 - 2022 "Instrument Transformers for Measurement Part 3: Power Current Transformer Verification Regulations": This regulation clearly standardizes multiple requirements for power current transformers including metrological performance, general technical specifications, and control of measuring instruments. 2. JJG 1157 - 2018 "Verification Regulations for DC Current Transformers": Specifically formulated for the verification of DC current transformers, covering metrological performance, technical indicators, verification conditions, verification items, verification methods, and handling of verification results.
3. JJG 313 - 2010 "Verification Regulations for Current Transformers for Measurement": Applicable to current transformers with rated frequency of 50Hz (or 60Hz), rated primary current ranging from 10A to 25000A, rated secondary current of 0.1A, 0.2A, 1A, 5A, and accuracy classes from 0.01 to 5. It covers initial verification, subsequent verification, and in-service inspection. (2) Enterprise Standards
1. QGDW 10572.1 - 2020 "Technical Specification for Instrument Transformers Part 1: Low Voltage Current Transformers" 2. QGDW 12093—2020 "Technical Specification for DC Bias Magnetic Resistance Calibration Devices"
(3) Standards to be Improved
1. Regarding the National Metrology Technical Specification "Verification Regulations for Instrument Transformers Part 9: DC Resistant Current Transformers": Although not yet officially released, the formulation of this specification will effectively fill the gap in verification standards for DC resistant current transformers.
2. Verification Regulations for Digital Comparison Current Transformer Calibrators: This regulation details the metrological performance, technical requirements, verification conditions, verification items, verification methods, and handling of verification results for digital comparison current transformer calibrators. It ensures the accuracy and reliability of these calibrators, providing an efficient tool for current transformer calibration.
3. Type Evaluation Outline for Wide Range Current Transformers: Specifies test items, test methods, and judgment criteria during the type evaluation process of wide range current transformers. These transformers can adapt to a broader range of current measurements.
4. Type Evaluation Outline for DC Resistant Current Transformers: Clarifies the requirements and methods for type evaluation of DC resistant current transformers. (4) Other Standards
1. JJF 1690 - 2018 "Current Transformer Calibration Specification": Details general requirements, calibration conditions, calibration items, calibration methods, and expression of calibration results for current transformer calibration. 2. DL/T 448 - 2016 "Technical Management Regulations for Electric Energy Metering Devices": Although not specifically a verification regulation for current transformers, it clearly defines requirements for configuration, selection, installation, acceptance, and periodic inspection of current transformers within electric energy metering devices.
3. NB/T 42084 - 2016 "Calibration Specification for Electronic Current Transformers": For this new type of product, it specifies technical requirements, calibration conditions, calibration items, calibration methods, and handling of calibration results. 3. Classification of Current Transformers (Sensors)
(1) Classification by Purpose 1. Current Transformers for Measurement: Mainly used in power systems for electric energy measurement and monitoring, requiring extremely high measurement accuracy and linearity to ensure precise and error-free energy measurement.
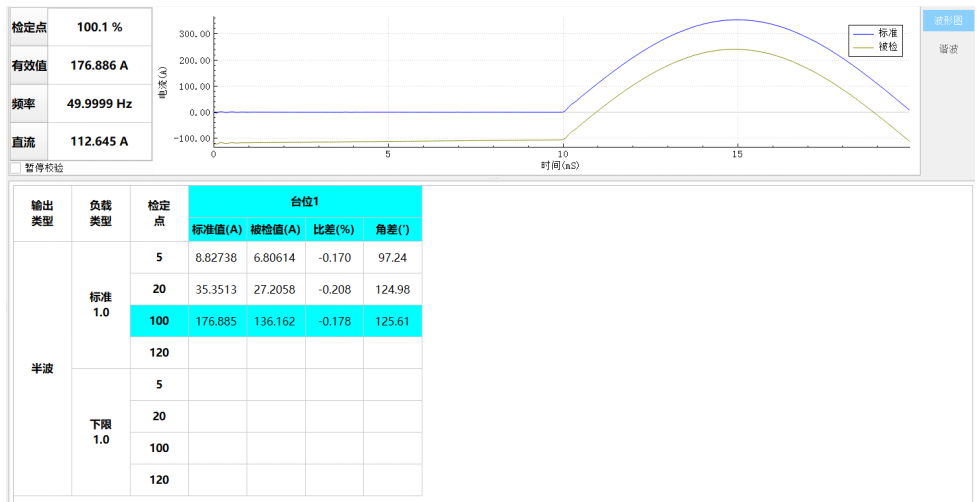
2. Current Transformers for Protection: Provide accurate current signals quickly to protection devices during power system faults, enabling timely operation to isolate faulty lines or equipment, ensuring safe and stable operation of the power system. They focus more on performance under fault conditions such as short circuits, including saturation characteristics and transient response.
(2) Classification by Principle 1. Electromagnetic Current Transformers: Operate based on electromagnetic induction principle, consisting of primary winding, secondary winding, and iron core. The primary winding is connected in series in the circuit; when primary current flows, alternating magnetic flux is generated in the iron core, inducing current in the secondary winding. This type is mature and widely used but has drawbacks such as iron core saturation, large size, and heavy weight.
2. Electronic Current Transformers: Divided into active and passive electronic current transformers. Active electronic current transformers use Rogowski coils or low power current transformers (LPCT) as sensors, converting signals to digital output via electronic circuits; passive electronic current transformers are based on optical principles, such as the Faraday magneto-optic effect, requiring no external power supply, offering good insulation and strong electromagnetic interference resistance, but are costly and have strict environmental requirements. (3) Classification by DC Resistance
1. Ordinary Current Transformers: 针对电子式电流互感器这一新型产品,规定了校准的技术要求、校准条件、校准项目、校准方法以及校准结果的处理。
三、电流互感器(传感器)分类
(一)按用途分类
1、测量用电流互感器:主要应用于电力系统中的电能计量与监测环节,对测量精度和线性度要求极高,以确保电能计量的精准无误。
2、保护用电流互感器:在电力系统发生故障时,迅速为保护装置提供精准的电流信号,促使保护装置及时动作,切除故障线路或设备,保障电力系统的安全稳定运行。其更侧重于在短路等故障情况下的性能表现,如饱和特性和暂态响应等。
(二)按原理分类
1、电磁式电流互感器:基于电磁感应原理工作,由一次绕组、二次绕组和铁芯构成。一次绕组串联于电路中,当一次电流通过时,铁芯中产生交变磁通,进而在二次绕组中感应出电流。该类型技术成熟,应用广泛,但存在铁芯饱和、体积大、重量重等弊端。
2、电子式电流互感器:分为有源电子式电流互感器和无源电子式电流互感器。有源电子式电流互感器利用罗氏线圈或低功率电流互感器(LPCT)等作为传感头,通过电子电路将信号转换为数字信号输出;无源电子式电流互感器基于光学原理,如法拉第磁光效应,无需外部电源,具备绝缘性能好、抗电磁干扰能力强等优势,但成本较高,对环境条件要求苛刻。
(三)按是否抗直流分类
1、普通电流互感器: Sensitive to DC components; in the presence of DC bias magnetization, its performance will be severely affected, potentially leading to increased measurement errors and protection malfunctions.
2. DC-resistant current transformer: Specifically designed to address the DC bias magnetization issue, it can effectively suppress the influence of DC components to a certain extent, ensuring good performance in AC current measurement and protection that contain DC components.
Related Products
XL-3600T6 Anti-DC Transformer Calibration System
XL-3610T3 Micro Current Transformer Calibration System
XL-3600T12H High-Precision Current Sensor Calibration System
XL-3620T6 Wide Range Current Transformer Calibration System
XL-3600T3 DC Current Sensor Calibration Bench








